In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, What is SEO in Digital Marketing where businesses compete for online visibility, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in driving organic traffic and improving a website’s ranking on search engines. SEO is not just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental strategy that can make or break an online business’s success. In this article, we’ll delve into the depths of SEO and how it fits into the realm of digital marketing.
Introduction to SEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of optimizing your website’s content, structure, and other elements to improve its visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The goal is to rank higher in organic (non-paid) search results for relevant keywords and phrases. By doing so, businesses can attract more targeted traffic to their websites, increase brand awareness, and ultimately drive conversions.
The Importance of SEO in Digital Marketing
In the competitive digital landscape, where millions of websites vie for attention, SEO Expert acts as a compass that guides search engines to your virtual doorstep. Without proper optimization, your website might get lost in the vast expanse of the internet, resulting in missed opportunities and potential customers.
What is SEO in Digital Marketing and How Search Engines Work
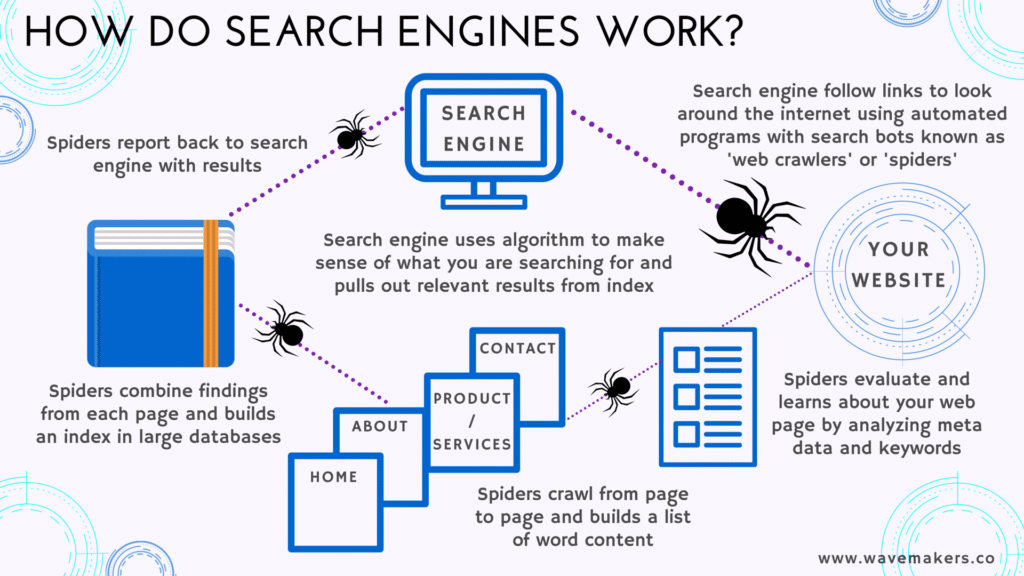
Before we dive into the intricacies of SEO, it’s essential to understand how search engines work. The process can be broken down into three main stages: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Crawling
Search engines use automated bots, known as crawlers or spiders, to scour the web for new and updated content. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, creating an index of web pages along the way.
Indexing
Once a page is crawled, it’s added to the search engine’s index, which is essentially a massive database of web pages. Indexing involves analyzing the content, keywords, and meta information of a page to understand its relevance to specific search queries.
Ranking
When a user enters a search query, the search engine’s algorithm sifts through its index to provide the most relevant and authoritative pages. These pages are then ranked based on various factors like keyword usage, content quality, and backlinks.
On-Page SEO: Optimizing Your Website
Effective on-page SEO involves a series of strategies to enhance your website’s individual pages. Let’s explore some key elements.
Keyword Research
Keywords are the foundation of SEO. Thorough keyword research helps you identify the terms and phrases your target audience is using to search for products or services like yours.
High-Quality Content
Creating informative, engaging, and valuable content not only attracts visitors but also encourages them to stay longer on your site. High-quality content is more likely to be shared and linked to, which can boost your SEO efforts.
Meta Tags and Descriptions
Meta tags, including title tags and meta descriptions, provide concise summaries of your page’s content. These tags appear in search results and influence click-through rates.
URL Structure
A clean and descriptive URL structure not only helps search engines understand your page’s content but also makes it more user-friendly.
Internal Linking
Internal links connect different pages within your website. They help distribute link equity, guide users to related content, and improve the overall user experience.
User Experience and Mobile-Friendliness
Search engines prioritize websites that provide a seamless user experience. Mobile-friendliness, fast loading times, and easy navigation contribute to higher rankings.
Off-Page SEO: Building Authority and Backlinks
Off-page SEO focuses on establishing your website’s authority and credibility across the internet.
Backlink Building Strategies
Backlinks, also known as inbound links, are links from other websites to yours. They signal to search engines that your content is valuable and authoritative.
Social Media Engagement
Active engagement on social media platforms can help increase your content’s visibility and attract more visitors to your website.
Influencer Outreach
Collaborating with influencers in your industry can introduce your website to a broader audience and generate valuable backlinks.
Technical SEO: Enhancing Site Performance
Technical SEO involves optimizing your website’s technical aspects for better search engine crawling and indexing.
Site Speed Optimization
Fast-loading websites provide a better user experience and are favored by search engines.
Mobile Optimization
Given the rise of mobile internet usage, optimizing your site for mobile devices is crucial for SEO success.
SSL and Security
Search engines prioritize secure websites. Installing an SSL certificate ensures data encryption and boosts your site’s credibility.
Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand your content better, leading to enhanced visibility in search results.
Local SEO: Reaching Nearby Customers
For businesses with a physical presence, local SEO helps attract customers in their vicinity.
Google My Business
Optimizing your Google My Business listing improves your chances of appearing in local search results and Google Maps.
Local Citations
Consistent business information across online directories strengthens your local SEO efforts.
Online Reviews
Positive online reviews not only build trust but also contribute to higher rankings in local search results.
Measuring SEO Success: Analytics and Metrics
Tracking and analyzing key metrics can provide insights into the effectiveness of your SEO strategies.
Organic Traffic
Monitoring the amount of traffic coming from organic search helps gauge the success of your SEO efforts.
Keyword Rankings
Tracking your keyword rankings over time helps identify which strategies are yielding positive results.
Click-Through Rates (CTRs)
High CTRs indicate that your page’s title and description are compelling to users.
Conversion Rates
Ultimately, the goal of SEO is to drive conversions. Monitoring conversion rates helps you understand your ROI.
The Evolving Nature of SEO
SEO is a dynamic field that continually evolves to match user behavior and search engine algorithms.
Voice Search Optimization
The rise of voice-activated devices requires optimizing your content for conversational queries.
AI and SEO
Artificial intelligence is transforming how search engines deliver results and how marketers approach SEO.
Algorithm Updates
Search engines regularly update their algorithms to provide users with the most relevant and high-quality results.
SEO vs. Paid Advertising: A Balancing Act
Both SEO and paid advertising have their merits and drawbacks.
Pros and Cons
SEO offers long-term benefits, while paid advertising can provide immediate visibility.
Budget Considerations
Balancing your budget between SEO and paid advertising depends on your business goals and timeline.
DIY SEO vs. Hiring Professionals
Deciding whether to handle SEO in-house or hire professionals depends on various factors.
Learning Curve
Learning SEO requires time and effort, but it can empower you to make informed decisions.
Time Investment
SEO is an ongoing process that demands consistent attention and adjustments.
Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Steer clear of these common SEO pitfalls.
Keyword Stuffing
Overloading your content with keywords can harm your rankings and readability.
Duplicate Content
Using duplicate content across multiple pages can lead to ranking issues.
Ignoring Mobile Users
Neglecting mobile optimization can lead to a poor user experience and lower rankings.
The Future of SEO: What to Expect
The future of SEO is exciting and filled with possibilities.
User Intent Optimization
Understanding and catering to user intent will become even more crucial for rankings.
Visual Search
Visual search technology will reshape how users discover content online.
Hyperlocal Targeting
Localized content will be essential as users seek information relevant to their immediate surroundings.
How do search engines work?
Search engines work by using automated programs, known as crawlers or spiders, to explore and index the vast amount of information available on the internet. These crawlers systematically navigate through web pages, following links from one page to another. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how search engines work:
- Crawling: Crawlers start by visiting a few web pages, often those with high authority or frequently updated content. They analyze the page’s content and follow the links within it to discover new pages. This process creates a network of interconnected web pages.
- Indexing: Once a page is crawled, its content is analyzed and stored in the search engine’s index. Think of the index as a massive database containing information about each page’s content, keywords, and other relevant data. Indexing helps search engines quickly retrieve relevant pages when a user enters a search query.
- Ranking: When a user enters a search query, the search engine’s algorithm scans its index to find pages that match the query’s keywords. The algorithm then ranks these pages based on various factors, including the page’s relevance, quality, and authority. Pages that are considered more relevant and trustworthy are ranked higher in the search results.
- Retrieval and Display: The search engine retrieves the highest-ranking pages from its index and displays them on the search engine results page (SERP). These results are often divided into different sections, such as organic results and paid advertisements. Users can then click on the search results that they find most relevant to their query.
- User Feedback Loop: Search engines continuously collect data on how users interact with search results. They track metrics like click-through rates (CTRs) and the time spent on a page after clicking on a result. This user feedback helps search engines refine their algorithms to provide more accurate and useful results over time.
- Algorithm Updates: Search engine algorithms are regularly updated to improve the quality of search results and adapt to changing user behavior. Algorithm updates can change how pages are ranked, encouraging website owners to adhere to best practices and provide valuable content.
In essence, search engines aim to connect users with the most relevant and authoritative content based on their search queries. The goal is to provide users with a seamless and efficient experience, enabling them to find the information they’re looking for quickly and easily.
Why SEO focuses on Google
SEO focuses on Google primarily because Google is the dominant search engine, commanding a significant share of the search market worldwide. Here are several reasons why SEO efforts often prioritize optimizing for Google:
- Market Share: Google’s search engine is the most widely used globally, with a market share of over 90% in many countries. This immense user base makes it crucial for businesses to optimize their websites for Google to reach a vast audience.
- Algorithm Sophistication: Google’s search algorithm is highly advanced and constantly evolving. It uses complex algorithms to analyze and rank web pages based on various factors like relevance, quality, and user experience. Optimizing for Google’s algorithm ensures that a website is more likely to rank well on other search engines as well.
- User Trust: Google has built a reputation for delivering relevant and high-quality search results. Users often trust Google’s recommendations, which means that websites ranking well on Google are perceived as reputable and authoritative sources.
- Innovation: Google continually introduces new features and technologies to enhance user experience and search results. This includes features like rich snippets, knowledge panels, and voice search integration. Optimizing for these innovations can provide a competitive advantage.
- Mobile and Voice Search: With the rise of mobile and voice search, Google remains at the forefront of adapting search technology to match changing user behavior. Optimizing for Google helps websites cater to mobile and voice search users effectively.
- Local Search: Google’s local search features, such as Google My Business, are essential for businesses targeting local customers. Optimizing for Google’s local search ensures visibility in local search results and on Google Maps.
- Algorithm Updates: Google frequently updates its search algorithm to provide better and more relevant results. While these updates can sometimes disrupt rankings, they also encourage websites to maintain high-quality content and user experience.
- Google Search Console: Google offers tools like Google Search Console that provide valuable insights into website performance, indexing status, and search appearance. These tools help website owners monitor and improve their SEO efforts.
- AdWords and Adsense: Google’s advertising platforms, such as Google AdWords and AdSense, are widely used by businesses to promote their products and services. SEO efforts can also complement and enhance the performance of these advertising campaigns.
- Global Reach: Google’s search engine reaches users across the globe, making it an essential platform for businesses with international audiences. Optimizing for Google helps businesses tap into a diverse range of markets.
While optimizing for Google is crucial, it’s also important to note that SEO practices are generally designed to improve a website’s overall visibility and performance across multiple search engines. While Google is the primary focus due to its dominance, well-executed SEO strategies often lead to improved rankings on other search engines as well.
What Google Wants: Understanding the Search Engine’s Priorities
Google, the world’s leading search engine, operates with a fundamental goal: to provide users with the most relevant, high-quality, and valuable information in response to their search queries. To achieve this, Google constantly refines its algorithms and updates its guidelines to ensure that websites meeting certain criteria are rewarded with higher search rankings. Here’s what Google wants from websites:
- Relevance: Google wants to match search queries with content that directly addresses the user’s intent. Websites should focus on creating comprehensive and relevant content that thoroughly covers the topic at hand.
- Quality Content: Google values well-written, informative, and authoritative content. It wants websites to provide content that adds value to users’ lives, answers their questions, and satisfies their information needs.
- User Experience: Google places a premium on websites that offer a positive user experience. This includes fast loading times, easy navigation, mobile-friendliness, and secure browsing (SSL certificates).
- Authority: Google aims to promote websites that are considered trustworthy and authoritative within their niche or industry. Building a strong online reputation through quality backlinks, positive reviews, and authoritative content is key.
- Originality: Google emphasizes originality and discourages duplicate or copied content. Websites should strive to create unique and original content that offers fresh insights and perspectives.
- Technical Excellence: Google wants websites to be technically sound, ensuring that crawlers can easily access and index their content. This involves optimizing site speed, fixing broken links, and using proper markup.
- Structured Data: Implementing structured data, such as schema markup, helps Google better understand the context of content and can lead to enhanced search results (rich snippets).
- E-A-T: Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T) are crucial factors in Google’s assessment of a website’s value. Demonstrating expertise and building trust in your niche are vital.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: With mobile devices being a primary source of internet access, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites. Responsive design and mobile optimization are essential.
- Engagement: Google measures user engagement signals, such as click-through rates (CTR), bounce rates, and time spent on page. Websites that engage users and keep them on the site tend to rank better.
- Natural Backlinks: While backlinks are important, Google values quality over quantity. Natural, relevant, and authoritative backlinks are more valuable than spammy or manipulative links.
- Safe Browsing: Google aims to protect users from malicious websites. Ensuring your website is secure and free from harmful content is essential.
- User Satisfaction: Ultimately, Google wants users to find what they’re looking for and have a positive experience. If users consistently find value in your content, it signals to Google that your website is meeting their needs.
Adhering to these principles not only aligns with what Google wants but also ensures that your website offers a valuable experience to users. By creating quality, relevant, and user-friendly content, you enhance your chances of ranking well in Google’s search results and providing genuine value to your audience.
How Google makes money
How Google Generates Revenue: Unveiling the Company’s Revenue Streams
Google, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., is renowned for its array of products and services that have transformed the digital landscape. It generates revenue through several key avenues, each contributing to its financial success. Here’s an overview of how Google makes money:
- Advertising: Google’s primary source of revenue is its advertising business. Through platforms like Google Ads (formerly AdWords), businesses pay to display their ads on Google’s search results pages, websites within the Google Display Network, YouTube, and other partner sites. Advertisers bid on keywords, and their ads are displayed to users whose search queries or browsing behavior match those keywords.
- Google Cloud Services: Google offers cloud computing services through Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It provides businesses with infrastructure, data storage, machine learning, and other services. Companies pay for these services based on usage, providing Google with a consistent stream of revenue.
- Hardware Sales: Google designs and sells hardware products like smartphones (Pixel), smart speakers (Google Home), and other devices (Nest, Chromecast). These sales contribute to its revenue and complement its ecosystem of software and services.
- Google Play Store: Google Play is the platform for Android app distribution. Developers pay fees to list their apps, and Google takes a percentage of revenue from in-app purchases and subscriptions made through the Play Store.
- YouTube: As one of the world’s largest video-sharing platforms, YouTube generates revenue through advertising. Advertisers can display ads before, during, or after videos, and YouTube shares a portion of the revenue with content creators.
- Subscription Services: Google offers subscription services like YouTube Premium and YouTube Music Premium, which provide an ad-free experience, offline playback, and exclusive content. These services generate recurring revenue.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Google offers productivity and collaboration tools through Google Workspace. Businesses pay for access to services like Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, and Google Sheets, often on a per-user basis.
- Google One: Google One is a subscription-based service that offers additional cloud storage for Google Drive, as well as other benefits like support and family sharing. Subscribers pay monthly or annually.
- Google Shopping: Google Shopping allows businesses to showcase their products in a dedicated section of Google’s search results. Businesses can pay to list their products and promote them to a wider audience.
- Digital Content Sales: Google Play also facilitates the sale of digital content such as movies, books, music, and apps. Google takes a percentage of revenue from these sales.
- Maps and Location Services: While Google Maps and other location-based services are offered for free to users, businesses can pay to feature their locations prominently on the map and provide targeted advertising to nearby users.
- Licensing and Partnerships: Google also earns revenue through licensing agreements and partnerships with other companies that use its technologies or integrate its services into their products.
In summary, Google’s diverse revenue streams encompass advertising, cloud services, hardware sales, subscription models, digital content sales, and more. These revenue sources collectively contribute to the company’s financial strength and enable it to continue offering innovative products and services to users around the world.
The Anatomy of Search Results: Understanding What You See on Google
When you enter a search query on Google or any other search engine, the page that displays the results is referred to as the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). This page is carefully designed to present a range of relevant information to the user in a clear and organized manner. Here’s a breakdown of the anatomy of search results:
- Search Box: At the top of the page, you’ll find the search box where you enter your query. This is where your journey begins.
- Search Query: After entering your query, it appears at the top of the SERP, reminding you of your search.
- Paid Ads (Sponsored Results): Often displayed at the top of the SERP and marked as “Ad,” these are paid advertisements. Advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their products or services, and their ads appear when those keywords are searched.
- Featured Snippet: A featured snippet is a highlighted block of text from a webpage that Google considers to have the most direct answer to the search query. It’s displayed prominently above the organic results.
- Knowledge Panel: On the right side of the page, you might see a knowledge panel, which provides brief information about a specific topic, entity, or person. This information is gathered from various sources and is intended to quickly answer common queries.
- Local Pack: If your search query has a local intent (e.g., “restaurants near me”), a local pack may appear. This displays a map with three local businesses and their details, such as reviews, address, and contact information.
- Organic Results: These are the main search results that appear below the paid ads. These results are ranked based on Google’s algorithms and are intended to provide the most relevant and valuable information to the user.
- Title: The title of the webpage appears as a clickable link. It’s usually an indication of the page’s topic and content.
- URL (Web Address): The URL indicates the specific web address of the page. It provides insight into the website’s structure and hierarchy.
- Description: The description provides a brief summary of the content found on the webpage. It’s designed to give users an idea of what they can expect if they click on the link.
- Site Links (Sitelinks): For some search results, Google might display additional links to specific pages within a website. These are meant to help users navigate directly to relevant sections of the site.
- Images and Videos: Depending on your search query, image and video results may also appear in the SERP. These visual elements can provide more context and variety to the results.
- Related Searches: At the bottom of the SERP, Google often suggests related search queries. These can help users refine their search or explore related topics.
- Pagination: If there are multiple pages of search results, pagination links may appear at the bottom, allowing you to navigate to the next page of results.
Remember that Google continuously updates its SERP layout and features to improve user experience and reflect changes in user behavior. This dynamic nature ensures that users receive the most relevant and valuable information in response to their queries.
The Role of SEO: Navigating the Digital Landscape
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a pivotal role in shaping the online presence and visibility of websites in the vast expanse of the internet. In an era where millions of websites compete for attention, SEO serves as a guiding compass, ensuring that businesses, organizations, and individuals can be found by their intended audience. Here’s an exploration of the key role that SEO plays:
- Enhancing Visibility: The primary objective of SEO is to enhance a website’s visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. By optimizing various elements of a website, such as content, keywords, and metadata, SEO helps the website appear in relevant search results when users enter related queries.
- Driving Organic Traffic: Organic traffic refers to visitors who arrive at a website through unpaid, natural search results. SEO is instrumental in attracting this type of traffic, as websites that rank higher in search results tend to receive more clicks and visitors.
- Targeting Relevance: SEO allows websites to target specific keywords and phrases that are relevant to their content, products, or services. By aligning with user search intent, websites can attract visitors who are actively seeking what they offer.
- Building Credibility and Trust: High search engine rankings are often associated with credibility and trustworthiness. Websites that appear on the first page of search results are perceived as authoritative sources, enhancing their reputation among users.
- User-Focused Optimization: Effective SEO involves creating content and designing websites with users in mind. User experience (UX) is a crucial factor, and SEO encourages practices like mobile optimization, fast loading times, and easy navigation.
- Balancing Technical and Creative Aspects: SEO requires a balance between technical optimization (e.g., site speed, mobile-friendliness) and creative content creation. Both aspects work together to provide a seamless experience for both users and search engine crawlers.
- Content Quality: SEO encourages the creation of high-quality, informative, and valuable content. This not only engages visitors but also attracts natural backlinks from other reputable websites, enhancing the website’s authority.
- Long-Term Sustainability: Unlike paid advertising, the effects of SEO are longer-lasting. Once a website achieves a good ranking, it can continue to generate organic traffic without ongoing ad expenditures.
- Measuring and Adapting: SEO involves continuous measurement and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs), such as organic traffic, keyword rankings, and bounce rates. This data informs adjustments to SEO strategies for better results.
- Competitive Advantage: In competitive industries, effective SEO can provide a competitive edge. Websites that consistently appear at the top of search results are more likely to attract users and outperform their rivals.
- Global Reach: SEO enables businesses to reach a global audience, breaking down geographical barriers and expanding their market reach.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While SEO requires an investment of time and effort, it is generally more cost-effective than paid advertising in the long run. Organic traffic generated through SEO is essentially free, aside from initial optimization efforts.
In a world where online visibility is crucial for success, SEO serves as a vital tool for websites to connect with their target audience, establish credibility, and thrive in the digital landscape. By aligning with search engines’ guidelines and user expectations, effective SEO strategies pave the way for meaningful online engagement and growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our journey through the world of search engines, SEO, and digital marketing has provided a comprehensive understanding of the intricate web that powers the online realm. From unraveling the mechanics of search engines to delving into the essential role of SEO, we’ve explored how these elements interconnect to shape the way we navigate and thrive in the digital landscape.
Search engines, led by the behemoth Google, serve as the gateway to a universe of information. They tirelessly crawl, index, and rank web pages, driven by the mission to deliver relevant and valuable content to users worldwide. The anatomy of search results, with its paid ads, organic listings, featured snippets, and knowledge panels, reflects the careful orchestration of algorithms and user-centric design to provide the best possible search experience.
Central to this ecosystem is SEO, a multifaceted strategy that empowers websites to rise above the digital noise. SEO’s role is more than just optimizing for search engines; it’s about creating a harmonious blend of technical prowess and user-centered content. By targeting relevance, driving organic traffic, and fostering credibility, SEO becomes the guiding compass for websites seeking visibility and engagement.
In a dynamic world where competition is fierce and user expectations are ever-evolving, understanding Google’s priorities becomes crucial. The pursuit of relevance, quality content, and an exceptional user experience underpin Google’s criteria for success. This approach resonates with the core tenets of digital marketing, where user satisfaction and value creation reign supreme.
As we navigate this ever-changing landscape, we recognize that Google’s revenue streams, driven by advertising, cloud services, hardware sales, and more, underpin its ability to innovate and lead. Behind the scenes, Google’s algorithms meticulously curate search results, bringing together paid and organic content, snippets of information, and insights from the web’s vast tapestry.
Ultimately, SEO emerges as the linchpin that ties everything together. It’s the bridge between user intent and web content, between search engine algorithms and website optimization. SEO empowers businesses to transcend geographical barriers, create lasting impressions, and engage audiences with authenticity and value.
In this digital age, understanding the intricacies of search engines, SEO, and Google’s ecosystem is more than just a curiosity; it’s an essential tool for success. Armed with this knowledge, individuals, businesses, and organizations can navigate the online realm with confidence, harnessing the power of technology to connect, communicate, and thrive.
FAQs
What is the primary goal of SEO?
The primary goal of SEO is to improve a website’s visibility on search engines and drive organic, targeted traffic.
How long does it take to see results from SEO efforts?
SEO is a gradual process, and it can take several months to see significant results. Patience and consistency are key.
Can I do SEO on my own, or should I hire a professional?
You can certainly learn and implement basic SEO strategies on your own. However, hiring professionals can provide expert insights and save you time.
What is the role of keywords in SEO?
Keywords are the terms and phrases users enter into search engines. Proper keyword usage helps search engines understand your content’s relevance to specific queries.
How often do search engine algorithms change?
Search engine algorithms undergo frequent updates, with major changes occurring a few times a year. Staying updated with industry news is essential.