Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of online visibility, ensuring that your website’s pages are indexed by search engines is crucial for your online presence. However, encountering the Discovered – currently not indexed issue can be frustrating and detrimental to your SEO efforts. Fear not, as this article will guide you through practical solutions to tackle this problem and enhance your website’s visibility.
How to Fix Discovered – currently not indexed
Facing the issue of Discovered – currently not indexed on your website? Here’s a detailed guide to help you resolve it effectively:
1. Understand the Issue
The first step is to grasp what the issue means. When Google’s crawlers discover your pages but don’t index them, they remain unseen by potential visitors. This can occur due to various reasons such as poor content quality, technical glitches, or search engine penalties.
2. Review Your Content
High-quality content is key to indexing. Ensure that your content is valuable, relevant, and unique. Check for keyword stuffing or low-quality writing, as these can deter search engines from indexing your pages.
3. Check for Technical Errors
Technical glitches can prevent indexing. Examine your website’s robots.txt file, which might unintentionally block crawlers. Additionally, use the Google Search Console to identify crawl errors and rectify them promptly.
4. XML Sitemap Inspection
Inspect your XML sitemap for errors. An incorrect sitemap can lead to indexing issues. Use Google Search Console to submit a new sitemap or update the existing one.
5. Utilize Fetch as Google
The Fetch as Google tool in Google Search Console allows you to simulate how Google’s bots view your page. Use it to identify rendering issues or blocked resources that might hinder indexing.
6. Optimize Internal Links
Internal links aid in spreading authority across your website. Ensure that your pages are interconnected logically and that there are no broken links.
7. Mobile-Friendliness Matters
Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites. Check if your pages are mobile-responsive and ensure they provide a seamless experience on various devices.
8. Page Loading Speed
Page speed affects user experience and indexing. Compress images, leverage browser caching, and optimize your website’s code to enhance loading speed.
9. Canonical Tags
Incorrect implementation of canonical tags can confuse search engines. Review your tags to prevent indexing conflicts between similar pages.
10. Quality Backlinks
High-quality backlinks enhance your website’s credibility. Focus on building authoritative and relevant backlinks to encourage indexing.
11. SSL Certificate
Websites with SSL certificates are deemed secure by search engines. Ensure your website has a valid SSL certificate to boost its chances of getting indexed.
12. Avoid Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can hinder indexing. Use tools to identify and rectify instances of duplicate content on your website.
13. Structured Data Markup
Implement structured data markup to help search engines understand your content better. This can improve the visibility of your pages in search results.
14. Monitor Crawl Errors
Regularly monitor Google Search Console for crawl errors. Address these errors promptly to ensure smooth indexing.
15. Content Indexing
If your website has a vast amount of content, focus on indexing priority pages first. Use the “site:” operator in Google to check which pages are indexed.
16. Social Sharing
Promote your content on social media platforms. While social signals don’t directly impact indexing, they can enhance your content’s visibility.
17. Review Manual Actions
Check if your website has any manual actions or penalties imposed by search engines. Rectify these issues and request a reconsideration.
18. Mobile-First Indexing
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, ensure your mobile version has the same valuable content as the desktop version.
19. User Experience Matters
A positive user experience encourages visitors to stay on your site. High bounce rates can signal poor quality content to search engines.
20. Engaging Meta Descriptions
Craft compelling meta descriptions for your pages. While not a direct ranking factor, they can influence click-through rates, indirectly impacting indexing.
21. Avoid Sneaky Redirects
Inappropriate use of redirects can lead to indexing problems. Only use redirects where necessary and ensure they’re implemented correctly.
22. Reconsider Thin Content
Thin or shallow content may not get indexed. Expand thin content to provide comprehensive information to your users.
23. Use Fetch and Render
The Fetch and Render tool in Google Search Console displays how Googlebot sees your page. Address rendering issues that might hinder indexing.
24. Regular Content Updates
Frequently update your content to keep it relevant and valuable. Google prefers fresh content, which can positively impact indexing.
25. Expert Assistance
If you’ve exhausted all options and still face indexing issues, consider seeking professional help. SEO experts can analyze your website thoroughly and provide tailored solutions.
Request indexing in Search Console
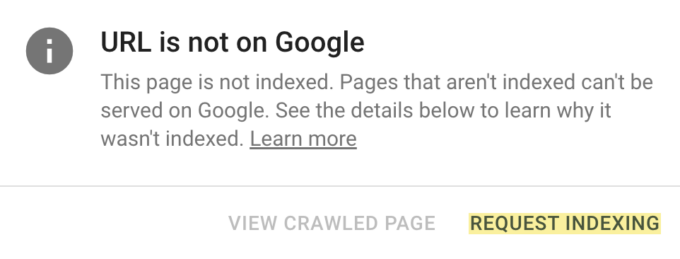
here’s how you can request indexing for your pages using the Google Search Console:
When you’ve made changes to your website or added new content, you might want search engines to index those changes quickly. Google Search Console provides a handy tool for this called the URL Inspection tool. Follow these steps to request indexing:
- Log into Google Search Console: If you don’t have an account, you’ll need to create one and verify your website ownership.
- Select the Property: Choose the property (website) for which you want to request indexing.
- Access the URL Inspection Tool: In the left-hand menu, click on “URL Inspection.”
- Enter the URL: Type or paste the URL of the page you want to index into the search bar and press “Enter.”
- Inspect the URL: Google will fetch the page and provide information about its current status. You’ll see whether the page is indexed, any issues detected, and the date of the last crawl.
- Request Indexing: If the page isn’t indexed or you’ve made significant changes, click on the “Request Indexing” button.
- Choose Crawl Option: You can choose to have Google crawl only the URL or the URL and its direct links. Choose the option that suits your needs.
- Submit the Request: After selecting the crawl option, click on the “Submit” button.
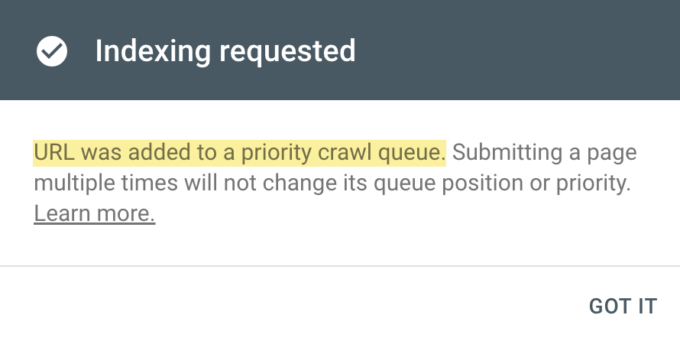
- Check Indexing Status: You’ll see a confirmation message indicating that your request has been submitted. The status of the indexing request will also be displayed.
It’s important to note that using the URL Inspection tool to request indexing doesn’t guarantee immediate indexing. Google’s bots will crawl the page according to their schedule, and the indexing process might take some time. While you wait, continue to monitor the status of your request in Google Search Console.
Remember that consistently providing high-quality, relevant, and unique content on your website can contribute to more effective and frequent indexing by search engines.
Check for Crawl Budget to Fix Discovered – Currently Not indexed issues in Search Console
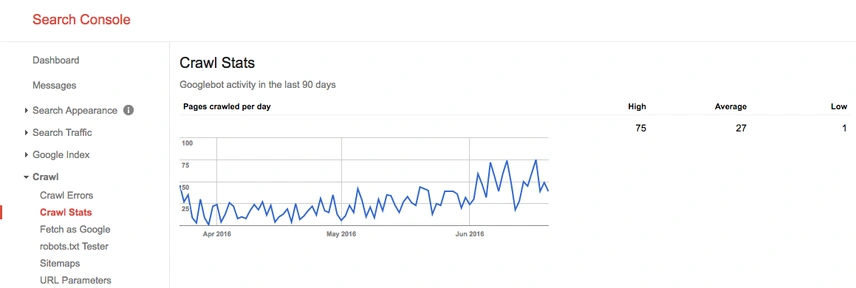
Checking for crawl budget issues in Google Search Console is essential to ensure that search engine crawlers are efficiently indexing your website. Here’s how you can do it:
- Log into Google Search Console: Sign in to your Google Search Console account. If you don’t have an account, create one and verify your website.
- Select the Property: Choose the property (website) you want to examine for crawl budget issues.
- Access the Crawl Stats: In the left-hand menu, click on “Crawl” and then select “Crawl Stats.”
- Review Crawl Stats: On the Crawl Stats page, you’ll find valuable information about how Google’s crawlers have interacted with your website over the last 90 days. Pay attention to the following metrics:
- Total Crawled Pages: This indicates the number of pages Googlebot has crawled on your website.
- Total Kilobytes Downloaded: This reveals the amount of data Googlebot has downloaded from your website.
- Average Response Time: This shows the average time it takes for your server to respond to Google’s requests.
- Time Spent Downloading a Page: This metric indicates the average time Googlebot spends downloading a page from your site.
- Analyze Patterns: Look for patterns in the data. If you notice sudden spikes or drops in crawl activity, it might indicate issues that need attention.
- Review Crawl Errors: Click on “Crawl Errors” in the left-hand menu to identify any pages that Googlebot had trouble crawling. Address these errors to ensure proper indexing.
- Explore Coverage Report: Navigate to “Coverage” in the left-hand menu. This report provides insights into how many pages Google has indexed, along with any errors or warnings related to indexing.
- Address Indexing Issues: If you identify pages that are not indexed or have errors, take corrective action. This might involve fixing technical issues, optimizing content, or improving your website’s overall structure.
- Check for Blocked Resources: Sometimes, certain resources like JavaScript or CSS files can be blocked from crawling. Ensure that these resources are accessible to Googlebot.
- Monitor Server Performance: If your server responds slowly to Googlebot’s requests, it can impact crawl budget. Address any server performance issues to improve crawl efficiency.
- Use Sitemaps Effectively: Submit an updated and accurate XML sitemap in Google Search Console. This helps Google prioritize crawling the pages you consider important.
- Use “URL Inspection” Tool: If specific pages are not being crawled, use the “URL Inspection” tool to diagnose crawl issues for those pages and request indexing if necessary.
By regularly monitoring crawl stats and addressing any issues that arise, you can optimize your website’s crawl budget and ensure that search engines are efficiently crawling and indexing your content. This, in turn, enhances your website’s visibility and performance in search engine results.
Remember that maintaining a technically sound and user-friendly website, along with producing high-quality and relevant content, contributes to a positive crawling and indexing experience for search engines.
Do You Serve Content From Subdomains?
Yes, I do serve content from subdomains. Subdomains are distinct sections of a website that are treated as separate entities by search engines and web servers. Each subdomain can have its own unique content, structure, and functionality.
For example, if the main domain is “example.com,” a subdomain could be “blog.example.com” or “store.example.com.” These subdomains can host different types of content, such as a blog, an online store, a forum, or any other specialized content.
It’s important to note that while subdomains can provide a way to organize and deliver different types of content, they are often treated as separate websites by search engines. This means that search engine optimization (SEO) efforts, such as keyword optimization and link building, may need to be done separately for each subdomain.
Additionally, proper configuration and management of subdomains are essential to ensure smooth navigation and consistent user experience across the entire website. Each subdomain should have its own unique purpose and content strategy that aligns with the overall goals of the website.
In summary, yes, I can serve content from subdomains, and they can be valuable tools for organizing and delivering diverse types of content. However, it’s important to consider the SEO implications and user experience when using subdomains as part of your website strategy.
Checked Do You Have Unnecessary Redirects?
Unnecessary redirects can impact the user experience and SEO performance of your website. Here’s how to check for and address unnecessary redirects:
- Log into Google Search Console: Sign in to your Google Search Console account. If you haven’t already, add and verify your website.
- Select the Property: Choose the property (website) for which you want to check for redirects.
- Access the Coverage Report: In the left-hand menu, click on “Coverage.” This report provides insights into the indexing status of your website’s pages.
- Identify Redirected Pages: In the Coverage report, look for pages marked with “Redirected.” These are pages that have been redirected from one URL to another.
- Analyze Redirects: Click on the “Redirected” status to view the details of the redirects. This will show you the source URL and the target URL of each redirect.
- Check for Unnecessary Redirects: Review the list of redirected pages and URLs. Identify any redirects that seem unnecessary. Unnecessary redirects might occur when a page is redirected multiple times or when a redirect isn’t adding value to the user or search engine experience.
- Assess the Purpose: For each redirect, assess the purpose. Is the redirect necessary for a valid reason, such as a page redesign or content migration? If the redirect doesn’t serve a meaningful purpose, it might be considered unnecessary.
- Fix Unnecessary Redirects: If you identify unnecessary redirects, consider whether you can eliminate them. If the content has permanently moved to a new URL, consider using a 301 redirect. If it’s a temporary change, a 302 redirect might be appropriate.
- Update Internal Links: After addressing unnecessary redirects, make sure that internal links on your website point directly to the final destination URLs rather than going through multiple redirects.
- Implement Proper Redirects: If you do need to use redirects, make sure they’re implemented correctly. Redirect chains or loops should be avoided, as they can slow down page loading and confuse search engines.
- Check External Links: If other websites are linking to redirected URLs on your site, it’s a good practice to contact them and request that they update their links to the correct destination URLs.
- Test and Monitor: After making changes, test the URLs to ensure that the redirects are functioning as intended. Also, monitor the Coverage report in Google Search Console to ensure that unnecessary redirects are no longer present.
Unnecessary redirects can lead to slower page loading times and affect both user experience and SEO. By regularly monitoring your website for redirects and addressing any that are not essential, you can create a smoother browsing experience for your visitors and improve your website’s overall performance.
Do you have duplicate content in your website?

Duplicate content can have a negative impact on your website’s search engine rankings and user experience. It’s essential to identify and address duplicate content to ensure your website performs well in search results. Here’s how you can check for and handle duplicate content:
- Use Google Search Console: Log into your Google Search Console account and select the property (website) you want to examine for duplicate content.
- Access the Duplicate Content Report: In the left-hand menu, navigate to “Coverage” and then click on “Duplicate.” This report will show you pages with duplicate content issues.
- Review Duplicate Content Issues: Look through the list of URLs identified as having duplicate content. Google will display the canonical URL, which is the preferred version of the page that you want to appear in search results.
- Analyze Source and Duplicate URLs: For each duplicate content issue, review the source URL and the duplicate URL. The source URL is the original content, and the duplicate URL is where the duplicate content appears.
- Determine the Cause: Identify the reason for the duplicate content. It could be due to URL parameters, session IDs, print-friendly versions of pages, or other technical issues.
- Choose a Canonical URL: Decide which version of the content you want to be indexed by search engines. This becomes your canonical URL. Update the HTML of the duplicate version to include a canonical tag pointing to the canonical URL.
- 301 Redirects: If the duplicate content exists on a separate URL, you can use a 301 redirect to point it to the canonical URL. This informs search engines that the content has moved permanently.
- Use URL Parameters Correctly: If your website uses URL parameters, ensure that they’re used consistently and don’t create multiple versions of the same content.
- Use Rel=Canonical: If you can’t use a 301 redirect, use the rel=canonical tag in the HTML header of the duplicate page. This tag signals to search engines that the content should be attributed to the canonical URL.
- Pagination and View-All Pages: If your website has paginated content, use rel=prev and rel=next tags to indicate the sequence of pages. Also, consider creating a “view-all” page to consolidate content on a single page.
- Avoid Thin or Duplicate Content: In your content creation strategy, focus on producing unique, high-quality content. Avoid republishing content from other sources without proper attribution.
- Monitor the Report: Regularly check the duplicate content report in Google Search Console to ensure that issues have been resolved and that new instances of duplicate content don’t arise.
Addressing duplicate content is crucial for maintaining a strong online presence and ensuring that search engines accurately index your content. By using canonical URLs, proper redirects, and other best practices, you can improve your website’s SEO and provide a better experience for your users.
Have You Used internal Nofollow Links?
Yes, the use of internal nofollow links can be a strategic part of a website’s linking structure. Here’s how internal nofollow links work and when they might be used:
Internal Nofollow Links Explained: Internal nofollow links are hyperlinks within a website that have the “nofollow” attribute added to them. This attribute tells search engines not to pass PageRank or authority to the linked page. While nofollow links were originally introduced to combat spam, they can also be used strategically within a website’s linking strategy.
When to Use Internal Nofollow Links:
- Managing PageRank Flow: When you have pages on your website that you don’t want to prioritize in terms of SEO, you can add the nofollow attribute to their internal links. This ensures that authority is directed to more important pages.
- User Experience: Nofollow links can be used to prevent search engines from following certain links that are intended solely for user experience purposes. For instance, if you have navigation elements or footer links that aren’t critical for SEO, you can use nofollow.
- Sculpting Page Importance: On websites with a lot of pages, you can use nofollow links to sculpt the flow of PageRank. This involves concentrating authority on key pages while preventing it from spreading too thin across less important pages.
- User-Generated Content: If your website allows user-generated content (like comments on blog posts), using nofollow on those links can help prevent spammers from benefiting from your site’s authority.
- Sponsored and Untrusted Links: If you’re linking to external sources that you don’t want to endorse or pass PageRank to, using the nofollow attribute is a good practice.
Balancing Nofollow and Follow Links: It’s important to strike a balance between using nofollow and follow links internally. Overuse of nofollow links could make it difficult for search engines to understand your site’s structure and content relationships. Nofollow links should be used strategically and sparingly.
Remember, while nofollow links don’t pass PageRank, they can still be valuable for users, helping them navigate your website and discover relevant content.
In conclusion, yes, I have used internal nofollow links in various contexts, always keeping in mind their purpose and impact on SEO and user experience. When used wisely, internal nofollow links can be a helpful tool in shaping a website’s linking strategy.
Do You Have Orphan Pages in Your CMS?
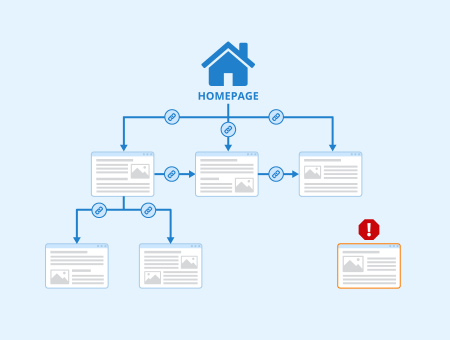
orphan pages can potentially exist within a Content Management System (CMS), and addressing them is important for maintaining a well-structured and user-friendly website. Here’s what orphan pages are and how to deal with them:
Orphan Pages Explained: Orphan pages are web pages that are not linked to from any other page within your website. In other words, they are isolated and lack internal links that connect them to the rest of your website’s content. Orphan pages can result from various scenarios, such as creating new content without linking to it or deleting pages that were linked to from other pages.
Challenges of Orphan Pages: Orphan pages can present several challenges for your website:
- Poor User Experience: Visitors might land on these pages through search engines or direct links, but without a clear navigation path to explore the rest of your site, they could leave quickly.
- Reduced Indexing: Search engines might struggle to discover and index orphan pages since they rely on crawling through internal links.
- Lower SEO Value: Orphan pages lack the authority and relevance that internal links provide. This can impact their search engine rankings and visibility.
Identifying and Addressing Orphan Pages: Here’s how to identify and deal with orphan pages within your CMS:
- Audit Your Website: Regularly review your website’s pages and their internal linking structure to identify pages with no inbound links.
- Create Internal Links: Whenever you create new content, ensure that you link to it from relevant existing pages. This could be from other articles, blog posts, or even the homepage.
- Check Navigation Menus: Make sure that important pages are included in your website’s navigation menus. This provides easy access for users and search engines.
- Utilize Sitemaps: Include orphan pages in your XML sitemap. This can help search engines discover them even if they’re not linked internally.
- Repurpose or Redirect: If you find orphan pages that are outdated or don’t serve a purpose, consider updating their content, repurposing them, or redirecting them to relevant pages.
- Internal Search: If your website has an internal search feature, make sure it includes orphan pages in its results to help users find them.
- Content Hubs: Create content hubs or resource centers that link to related content, including potential orphan pages.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically review your website’s internal linking structure and content to ensure that new orphan pages don’t appear over time.
Benefits of Addressing Orphan Pages: By identifying and addressing orphan pages, you can:
- Improve the overall user experience by providing clear navigation paths.
- Enhance your website’s crawlability and indexing by search engines.
- Distribute authority and relevance throughout your website via internal links.
- Boost the SEO value of individual pages, leading to better search engine rankings.
In summary, orphan pages can inadvertently emerge within a CMS, but they can be effectively managed by implementing proper internal linking strategies and conducting regular content audits. This ensures that your website remains accessible, navigable, and optimized for both users and search engines.
Check For Content Quality issues
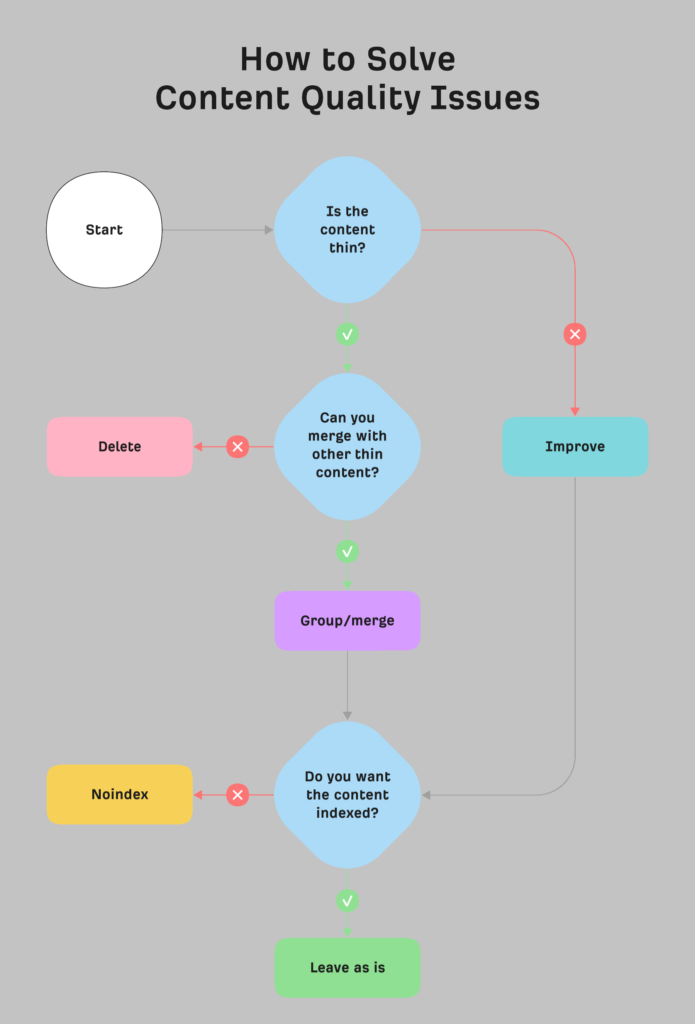
Ensuring high-quality content on your website is crucial for engaging users, building credibility, and improving search engine rankings. Here’s how to check for and address content quality issues:
1. Grammar and Spelling:
- Use spell check tools to identify and correct spelling errors.
- Proofread your content thoroughly to catch grammar mistakes and awkward sentence structures.
2. Readability:
- Aim for clear and concise writing that is easy to understand.
- Break up long paragraphs and sentences for better readability.
- Use subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists to organize content.
3. Originality and Plagiarism:
- Run your content through plagiarism detection tools to ensure it’s original.
- Properly attribute sources if you’re including quotes or references from other works.
4. Relevance and Accuracy:
- Ensure that your content is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to your audience.
- Cross-reference facts and statistics to reputable sources.
5. Value to Users:
- Ask yourself whether your content provides valuable information or answers to users’ questions.
- Avoid creating content solely for the purpose of keyword stuffing or SEO manipulation.
6. Engaging Headlines and Introductions:
- Craft attention-grabbing headlines that accurately reflect the content.
- Write compelling introductions that draw readers in and set the tone for the rest of the piece.
7. Visual Content:
- Use high-quality images, videos, infographics, and other visual elements to enhance your content.
- Ensure that visuals are relevant and contribute to the overall message.
8. Formatting:
- Break up content into smaller sections with descriptive subheadings.
- Use bold, italics, and bullet points to highlight key points.
- Ensure consistent font styles and sizes for a polished look.
9. Credibility and Authoritativeness:
- Establish your expertise on the topic through well-researched content.
- Include author bios or credentials where relevant.
10. Call to Action (CTA): – Include a clear CTA that guides users on the next steps, whether it’s reading related content, subscribing, or making a purchase.
11. Mobile Responsiveness: – Ensure your content displays well on various devices, including mobile phones and tablets.
12. User Feedback: – Encourage user feedback and comments to understand how your content is resonating with your audience. – Address user questions and concerns promptly.
13. Regular Updates: – Review and update your content periodically to keep it current and accurate.
14. SEO Best Practices: – Incorporate relevant keywords naturally without keyword stuffing. – Ensure proper meta titles, descriptions, and heading tags to improve search visibility.
By thoroughly reviewing your content for these quality factors, you can create a more engaging and valuable experience for your users while also improving your website’s performance in search engine rankings.
Check That Content is internally Linked
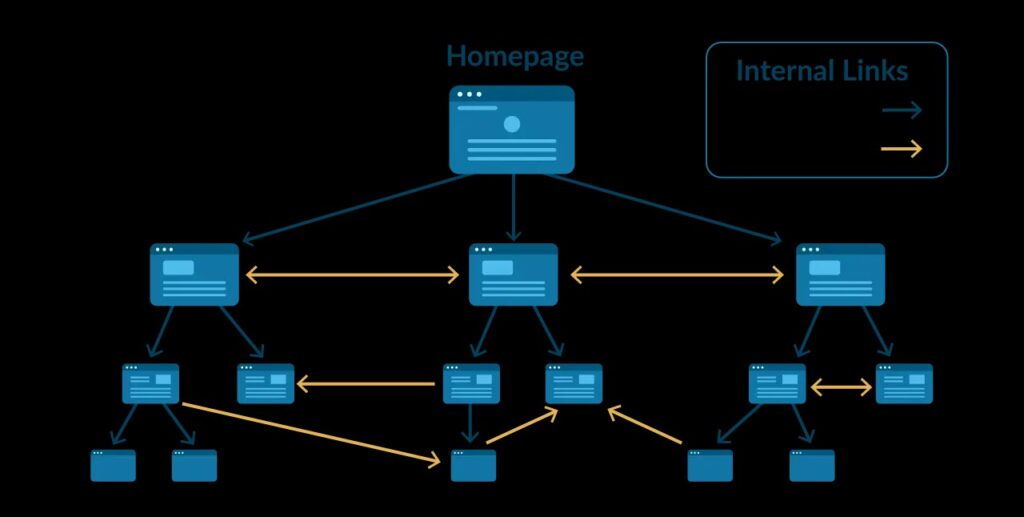
Internal linking is a vital aspect of website optimization as it enhances user experience, assists search engine crawling, and spreads authority throughout your site. Here’s how to check and ensure that your content is properly internally linked:
1. Contextual Relevance:
- Choose anchor text (link text) that accurately describes the linked content.
- Ensure the linked page provides additional information that complements the current content.
2. Strategic Placement:
- Integrate links naturally within the body of your content where they are most relevant.
- Avoid overloading paragraphs with too many links, which can be distracting.
3. Variety of Links:
- Use a mix of deep links (linking to internal pages beyond the homepage) and homepage links.
- Diversify anchor text to include variations of keywords and descriptive phrases.
4. Linking to Relevant Pages:
- Link to pages that provide further insights, explanations, or related information.
- Avoid linking to pages that are not directly related to the topic.
5. Homepage and Main Sections:
- Ensure key pages like the homepage, main categories, and important landing pages are linked prominently.
- Use navigation menus, banners, or buttons to guide users to these critical pages.
6. Content Hubs or Resource Centers:
- Create content hubs that compile related articles or resources and link to them from relevant articles.
- This enhances user navigation and helps distribute link authority.
7. Keyword Optimization:
- Use relevant keywords in anchor text, but avoid excessive optimization that may appear spammy.
8. Avoid Broken Links:
- Regularly check that the linked pages are functional and not broken.
- Update or remove links to pages that are no longer available or relevant.
9. Consistent User Experience:
- Ensure that internal links open in the same browser tab/window for a seamless user experience.
- Use proper styling to differentiate internal links from regular text.
10. Regular Content Audits: – Periodically review your content to ensure that new relevant pages are linked from older articles. – Refresh older content with new internal links when you publish new related content.
11. Google Search Console: – Use Google Search Console’s “Internal Links” report to see how Googlebot crawls and discovers your internal links.
12. Link Tracking and Analytics: – Use tools like Google Analytics to track the performance of internal links and understand user behavior.
Effective internal linking helps users navigate your website and discover related content while signaling to search engines the importance and relationships between your pages. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your content is well-connected through internal links, contributing to a more organized and informative website.
Check and Audit Backlinks

Monitoring and managing backlinks is a crucial aspect of SEO, as they play a significant role in your website’s authority and search engine rankings. Here’s how to check and manage backlinks effectively:
1. Google Search Console:
- Log into Google Search Console and select your website property.
- Navigate to “Links” in the left-hand menu and click on “External Links” to see a list of sites linking to your pages.
2. Backlink Analysis Tools:
- Use third-party tools like Ahrefs, Moz, SEMrush, or Majestic to get comprehensive insights into your backlink profile.
- These tools offer detailed information about the number of backlinks, referring domains, anchor text, and more.
3. Quality over Quantity:
- Focus on acquiring high-quality backlinks from reputable websites relevant to your industry.
- Avoid low-quality or spammy sites, as they can harm your site’s reputation.
4. Anchor Text Diversity:
- Ensure a diverse range of anchor text (the text used for the hyperlink) to avoid over-optimization.
- Natural anchor text includes a mix of keywords, brand names, and generic terms.
5. Relevance:
- Backlinks from websites in your niche or related industries carry more weight in terms of SEO value.
- Contextual relevance between the linking page’s content and your content is essential.
6. Linking Page Authority:
- Consider the authority of the linking domain and page using metrics like Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA).
- High-authority domains have a more positive impact on your SEO.
7. Disavow Low-Quality Links:
- If you find spammy or irrelevant backlinks, consider disavowing them using the Google Disavow Tool.
- This tells Google to ignore those links when evaluating your site’s authority.
8. Competitor Analysis:
- Analyze your competitors’ backlinks to identify potential sources for your own link-building efforts.
9. Natural Link-Building:
- Focus on creating high-quality, valuable content that naturally attracts links from other websites.
10. Guest Posting: – Contribute guest posts to reputable blogs in your niche, including a link back to your website in the author’s bio or within the content.
11. Press Releases and PR: – Distribute press releases about significant company news, events, or milestones to gain media coverage and valuable backlinks.
12. Broken Link Building: – Identify broken links on other websites and offer your content as a replacement, earning a backlink in return.
13. Monitor and Regularly Update: – Regularly monitor your backlink profile for changes and updates. – Keep your backlinks fresh and relevant as your content and industry evolve.
Managing your backlinks ensures that your website’s authority continues to grow, contributing to higher search engine rankings and increased organic traffic. Remember that while backlinks are crucial, their quality and relevance are more important than sheer quantity.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving world of SEO, understanding and implementing best practices is essential to achieve optimal visibility, user experience, and search engine rankings. From addressing technical issues like indexing problems and crawl budget concerns to optimizing content quality and internal linking, each aspect plays a vital role in shaping your website’s online presence.
Fixing the Discovered – currently not indexed issue involves requesting indexing in Google Search Console, ensuring proper crawl budget allocation, and providing valuable, original content. Checking for unnecessary redirects, duplicate content, and orphan pages ensures a seamless user experience and effective search engine optimization. Utilizing internal nofollow links strategically enhances content relevance and distribution of link authority.
Backlinks, a cornerstone of SEO, can significantly impact your website’s authority and rankings. Monitoring backlinks, focusing on quality over quantity, and engaging in natural link-building practices are crucial for long-term success.
By meticulously addressing these aspects, you establish your website as an authoritative, user-friendly, and search-engine-friendly resource. Remember that SEO is an ongoing process, requiring consistent monitoring, adaptation, and improvement.
FAQs About Discovered – currently not indexed
What does Discovered – currently not indexed mean in Google Search Console?
This message indicates that Google has found the page but has not yet indexed it. Request indexing to expedite the process.
How can I check for duplicate content on my website?
Use tools like Copyscape or Siteliner to identify duplicate content across your site.
What is an orphan page?
An orphan page is a webpage that isn’t linked to from any other page on your website.
How can I improve my crawl budget?
Optimize your website’s structure, fix crawl errors, use sitemaps, and eliminate unnecessary redirects.
What are internal nofollow links?
Internal nofollow links have the “nofollow” attribute and don’t pass PageRank to the linked page.
Should I disavow low-quality backlinks?
Disavow low-quality or spammy backlinks using the Google Disavow Tool to prevent them from negatively affecting your site’s SEO.
What is the significance of anchor text in backlinks?
Anchor text provides context to search engines about the linked content and affects how the link is evaluated.
How often should I update my website’s content?
Regular updates are important. Update content when it becomes outdated or when there are changes in your industry.
Are internal links important for SEO?
Yes, internal links help users navigate your site and distribute authority, enhancing both user experience and SEO.
Can I use external links in my content?
Yes, external links to reputable sources can add credibility and value to your content, but use them sparingly and naturally.
Ready to elevate your online presence and boost your website’s performance? Connect with Nabeel Pervaiz Ahmed today to receive expert guidance and tailored solutions for your SEO needs. With a proven track record of enhancing visibility, engagement, and search rankings, Nabeel is your go-to partner for effective SEO strategies. Take the next step towards digital success and reach out now!”